The Understanding DMARC, DKIM, and SPF: Essential Email Authentication Protocols
In an age where email communication is a cornerstone of business operations, ensuring the security and integrity of your email messages is paramount. Cyber threats such as phishing and spoofing are on the rise, making it essential for organizations to implement robust email authentication protocols. Three key technologies that play a crucial role in email security are DMARC, DKIM, and SPF. In this blog post, we’ll explore what these protocols are, how they work, and why they are vital for protecting your organization’s email communications.
What is SPF (Sender Policy Framework)?
SPF, or Sender Policy Framework, is an email authentication protocol that helps prevent spoofing by allowing domain owners to specify which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of their domain. By publishing an SPF record in the Domain Name System (DNS), organizations can define a list of IP addresses or hostnames that are permitted to send emails for their domain. When an email is received, the recipient’s mail server checks the SPF record to verify that the email comes from an authorized source. If the sending server is not listed, the email may be marked as spam or rejected, reducing the risk of fraudulent emails reaching recipients.
What is DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)?
DKIM, or DomainKeys Identified Mail, is another email authentication method that adds a digital signature to outgoing emails. This signature is generated using a private key held by the sender and is included in the email header. When the email is received, the recipient’s mail server can retrieve the sender’s public key from the DNS to verify the signature. If the signature matches, it confirms that the email has not been altered in transit and that it genuinely comes from the claimed domain. DKIM helps ensure the integrity of the email content and provides recipients with confidence that the message is legitimate.
What is DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)?
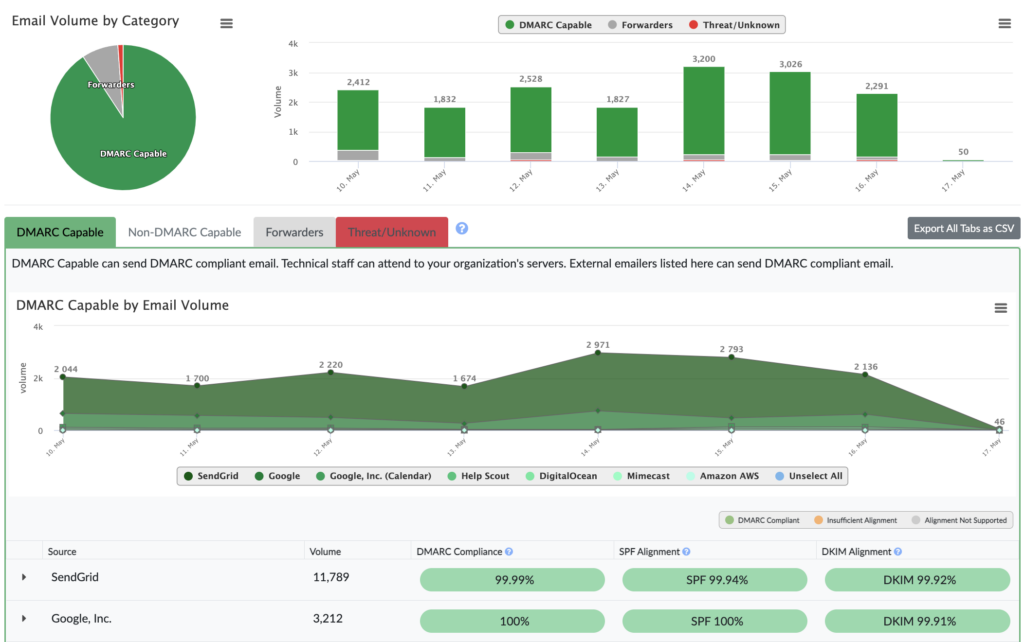
DMARC, or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance, builds on the foundations of SPF and DKIM by providing a framework for email authentication and reporting. DMARC allows domain owners to specify how their emails should be handled if they fail SPF or DKIM checks. By publishing a DMARC record in the DNS, organizations can instruct receiving mail servers to either quarantine or reject emails that do not pass authentication checks. Additionally, DMARC provides reporting features that allow domain owners to receive feedback on email authentication results, helping them monitor and improve their email security posture.
Why Are DMARC, DKIM, and SPF Important?
Protect Against Phishing and Spoofing: Implementing DMARC, DKIM, and SPF significantly reduces the risk of phishing attacks and email spoofing, protecting both your organization and your recipients.
Enhance Email Deliverability: By authenticating your emails, you improve the chances of your legitimate messages reaching the inbox rather than being marked as spam.
Build Trust with Recipients: When recipients see that your emails are authenticated, they are more likely to trust your communications, enhancing your brand’s reputation.
Gain Visibility and Control: DMARC reporting provides valuable insights into your email traffic, allowing you to identify unauthorized use of your domain and take corrective action.
Conclusion
Incorporating DMARC, DKIM, and SPF into your email strategy is essential for safeguarding your organization’s communications and protecting your brand’s reputation. By implementing these email authentication protocols, you can significantly reduce the risk of email fraud, enhance deliverability, and build trust with your recipients. If you haven’t already, now is the time to take action and secure your email communications with DMARC, DKIM, and SPF. For assistance in setting up these protocols, contact us today to learn how we can help you strengthen your email security.